Understanding Senior Fitness Training
As society acknowledges the importance of an active lifestyle for all age groups, a particular emphasis has been placed on senior fitness training. It serves as a pivotal aspect of retaining independence, enhancing quality of life, and reducing the risks of chronic diseases. Engaging in a tailored Senior Fitness Training program can lead to healthier, more vibrant living for older adults. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key elements of senior fitness training, addressing its importance, common challenges faced by older adults, and practical strategies to enhance physical fitness.
The Importance of Physical Fitness for Seniors
Maintaining physical fitness is crucial for seniors as it can greatly influence their overall health and well-being. Regular exercise helps to:
- Enhance Muscle Strength: Aging leads to muscle loss, making strength training essential. Stronger muscles contribute to better balance and reduced fall risk.
- Improve Cardiovascular Health: Activities that elevate heart rate, such as walking or cycling, ensure better circulation and heart health, decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Boost Mental Health: Physical activity releases endorphins, improving mood and reducing feelings of depression or anxiety. This is especially impactful given the increasing instances of loneliness among seniors.
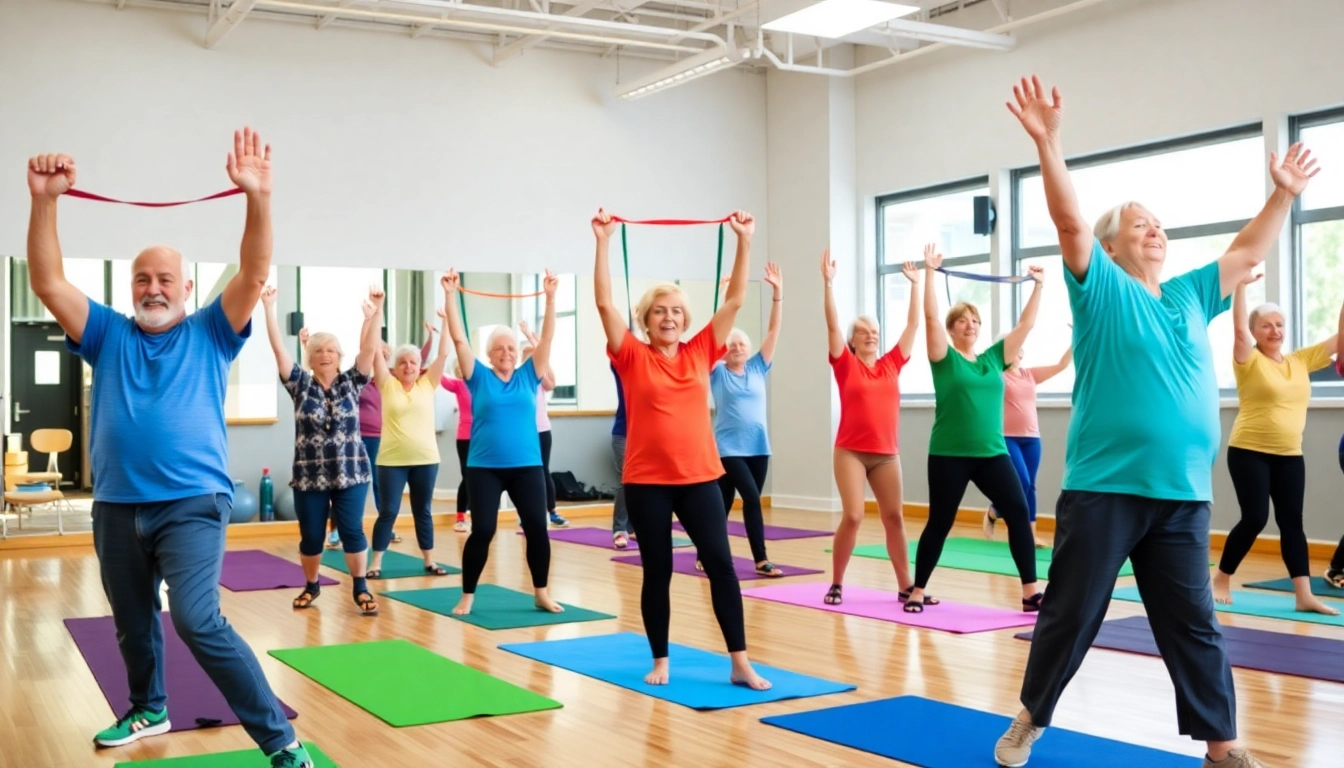
- Foster Social Connections: Group fitness classes provide social opportunities that can help counter isolation and loneliness, promoting emotional well-being.
Incorporating physical fitness into daily routines can lead to a more fulfilling life, allowing seniors to pursue hobbies and activities they enjoy with greater energy and enthusiasm.
Common Challenges Faced by Older Adults
Despite the myriad benefits associated with senior fitness training, many older adults face unique challenges that may hinder their ability to stay active. These include:
- Physical Limitations: Injuries, arthritis, and chronic diseases can restrict mobility and affect exercise choices.
- Lack of Motivation: Many seniors may feel overwhelmed or unclear about which workouts are appropriate for their age group.
- Fear of Injury: The fear of falling or sustaining an injury often inhibits seniors from joining fitness classes or engaging in physical activities.
- Access to Resources: Limited access to fitness facilities or knowledgeable trainers can deter many seniors from participating in exercise programs.
By understanding these challenges, caregivers, fitness trainers, and the seniors themselves can develop strategies to overcome these barriers and encourage consistent physical activity.
Setting Realistic Fitness Goals
Goal-setting is a crucial component of any fitness program. Establishing realistic and achievable goals helps seniors stay motivated and provides a clear roadmap for personal progress. Here are essential steps for effective goal setting:
- Start Small: It’s vital to begin with manageable goals, such as taking short daily walks or attending a low-impact exercise class.
- Make Goals Specific: Rather than vague targets like “get fit,” opt for specific goals, such as “walk for 20 minutes, three times a week.”
- Track Progress: Use a journal or fitness app to monitor achievements, which can boost motivation and provide accountability.
- Adjust Goals as Necessary: Goals should be adaptable to changing abilities and circumstances. Celebrate small victories and adjust the plan to reflect new challenges or successes.
Key Components of Effective Fitness Programs
An effective senior fitness training program incorporates a variety of exercise components to ensure comprehensive physical improvement. Understanding the key components can help in designing a well-rounded fitness routine.
Balance and Flexibility Exercises
Balance and flexibility are critical for preventing falls and maintaining mobility. Exercises targeting these areas include:
- Chair Yoga: This gentle form of yoga allows seniors to improve flexibility without the strain of standing poses.
- Tai Chi: Often referred to as “meditation in motion,” Tai Chi enhances balance through slow, deliberate movements.
- Resistance Band Workouts: Using resistance bands can significantly improve flexibility and strengthen muscles without risking injury.
Strength Training Essentials for Seniors
As mentioned, strength training is vital for combatting muscle loss and improving overall body strength. Key guidelines for strength training in seniors include:
- Start with Bodyweight Exercises: Activities like squats, push-ups, and lunges can improve strength without the need for weights.
- Utilize Light Weights or Resistance Bands: Once comfortable with bodyweight exercises, incorporating light dumbbells or bands can further enhance strength.
- Focus on Major Muscle Groups: Prioritize exercises that engage multiple muscle groups, such as deadlifts and bench presses.
- Training Frequency: Aim for at least two days a week dedicated to strength training, allowing a day of rest in between.
Aerobic Activities: Keeping the Heart Healthy
Aerobic exercises are essential for improving cardiovascular health. Here are some accessible aerobic activities suitable for seniors:
- Walking: One of the easiest and safest forms of exercise for seniors, walking can be done indoors or outdoors.
- Water Aerobics: The buoyancy of water reduces the risk of injury and supports joints while providing resistance for strength training.
- Cycling: Stationary bikes or outdoor cycling can increase cardiovascular capacity and leg strength.
Creating a Personalized Senior Fitness Training Plan
Designing a personalized training plan is critical for ensuring the program meets individual needs, limitations, and fitness goals.
Assessing Individual Fitness Levels
Before starting any fitness program, it’s important to assess the individual’s current fitness level. This can involve:
- Medical Consultation: A physical examination can help identify health concerns that need to be acknowledged in the training plan.
- Physical Fitness Tests: Simple assessments, like timed walking tests or flexibility measurements, can establish baselines for strength and endurance.
Choosing the Right Type of Exercises
The right exercises depend on individual preferences, current fitness levels, and any physical limitations. When selecting exercises, consider the following:
- Enjoyment: Choose activities that the individual finds enjoyable to ensure long-term engagement.
- Diversity: Incorporate a variety of workouts (strength, balance, flexibility) to promote overall fitness and prevent boredom.
- Functional Movements: Focus on exercises that improve everyday activities, such as sitting down, picking things up, or climbing stairs.
Progress Tracking and Adjustments
Regularly tracking progress is fundamental in maintaining motivation and effectiveness of the training plan. Key techniques include:
- Set Check-Ins: Schedule consistent check-ins to review goals, fitness levels, and any changes needed in the program.
- Celebrate Milestones: Recognize achievements to inspire continued effort and enthusiasm.
- Adjust as Needed: Modify the fitness plan based on progression or new challenges, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
Nutrition and Senior Fitness Training
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting an active and healthy lifestyle. Seniors should ensure their diet aligns with their fitness efforts.
Dietary Needs for Active Seniors
Older adults often require adjusted nutrient intake to support their fitness activities:
- Protein-Rich Foods: Important for muscle recovery and growth. Examples include lean meats, legumes, and dairy.
- Whole Grains: Foods like whole grain bread, brown rice, and oats provide sustained energy for workouts.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Essential for vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help with recovery and overall health.
Hydration Tips During Workouts
Staying hydrated is crucial, particularly during physical activity. Here are some helpful tips:
- Drink Before, During, and After Exercise: Ensure adequate hydration to facilitate performance and recovery.
- Choose Water or Electrolyte Drinks: Water is often sufficient, but electrolyte drinks can be beneficial for longer activities.
Meal Planning for Optimal Energy
Proper meal planning can help seniors maintain energy levels throughout the day:
- Regular Eating Schedule: Aim for balanced meals at consistent times to ensure steady energy supply.
- Pre-Workout Snacks: Consume light snacks such as yogurt or a banana before workouts to sustain energy levels.
- Post-Workout Nutrition: Incorporate protein and carbohydrates in post-workout meals for optimal recovery.
Resources and Support for Seniors in Fitness Training
It’s essential for seniors to have access to resources and support to maximize their fitness journey. Various options can aid in achieving fitness goals.
Finding Certified Trainers Specializing in Seniors
Working with certified trainers who specialize in senior fitness can provide tailored guidance and support. Look for trainers with credentials from recognized organizations, such as:
- AFAA (Athletics and Fitness Association of America)
- ACE (American Council on Exercise)
- ISSA (International Sports Sciences Association)
Community Programs and Class Opportunities
Community centers often offer fitness programs designed specifically for seniors. Local classes might include:
- Chair Yoga or Pilates Classes: Gentle classes accommodating various mobility levels.
- Aquatic Classes: Low-impact water exercises suitable for strengthening and rehabilitation.
- Walking Groups: Organized community walks provide motivation and social interaction.
Using Technology for Home Workouts
Technology can enhance access to fitness resources. Examples include:
- Fitness Apps: Many apps offer specialized programs for seniors with guided workouts.
- YouTube Channels: Channels dedicated to senior fitness can provide a variety of workouts at home.
- Virtual Personal Training: Online trainers can customize workouts to fit individual abilities and preferences.